Foundry Definition and Methods of Hand Mold
Definition of hand mold:
Hand mold is a modeling process that is all done by hand or hand tools. Hand mold operation is flexible, wide adaptability, simple process equipment, low cost. However, its casting quality is poor, productivity is low, labor intensity is high, and the technical requirement is high. Therefore, hand mold is mainly suit for single-piece small batch production, especially heavy and complex shaped castings.
Methods of hand mold:
1. According to the different characteristics of the sand mould:
Two-box modeling, three-box modeling, off-box modeling, pit modeling, core assembly modeling.
2. According to the different characteristics of the appearance:
Full mold modeling, split mold modeling, sand excavation modeling, fake box modeling, live block modeling.
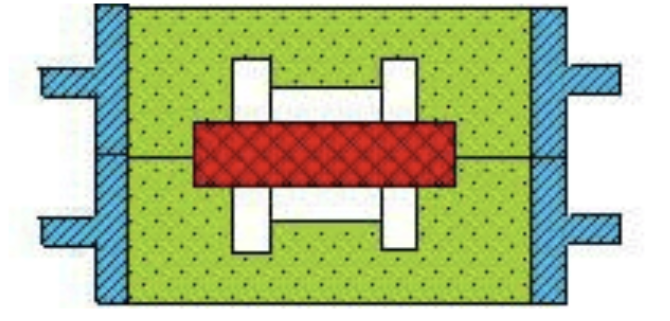
1) Two-box modeling
Two-box modeling is the most basic method of modeling. The mold is composed of a pair of upper and lower molds, which is easy to operate. Suitable for various production batches and various sizes of castings
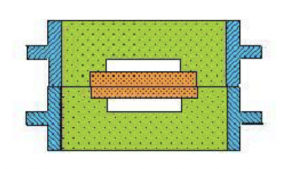
2) Three-box modeling
The three-box modeling mold is composed of upper, middle and lower molds. The middle height needs to be compatible with the distance between the two parting surfaces of the casting. Three-box modeling operation costs labor. It is mainly suitable for single-piece, small batch production castings with two parting surfaces.
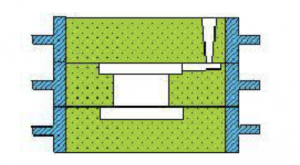
3) Off-box modeling
The off-box moulding is mainly used for moulding with movable sand box. After the mould is closed, the sand box is taken out and used for moulding again. One sand box can produce many molds. In order to prevent wrong moulding during metal pouring, you should use moulding sand to fill the mould around tightly. The mould can also be boxed. It is often used to produce small castings. Because the sand box has no box belt, the sand box is generally less than 400mm.
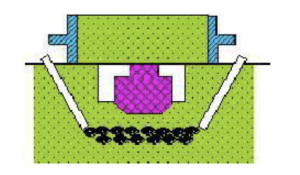
4) Pit modeling
The pit modeling uses the workshop ground sand bed as the lower box of the mold. Large castings need to be covered with coke under the sand bed, and the air outlet pipe should be buried in order to bleed air during casting.
5) Core assembly modeling
Core assembly modeling is to combine several sand cores into a mold without the need for a sand box. It can improve the accuracy of castings, but the cost is high. What are the manual molding methods suitable for mass production of complex sand castings?
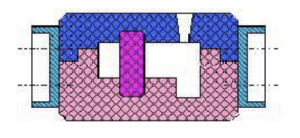
6) Full mold modeling
The shape of the full mold modeling is integral, the parting surface is flat, and the mold cavity is all in half of the mold. The shape is simple and the casting will not produce wrong mold defects. It is suitable for castings with the largest section of the casting at the end and flat.
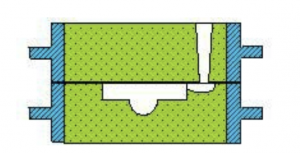
7) Sand excavation modeling
The appearance of sand excavation modeling is integral, but the parting surface of the casting is curved. In order to facilitate the manual digging of the sand that hinders the starting of the mold, the modeling is labor-intensive, the productivity is low, and the technical level of the workers is high. Used for single-piece, small-batch production castings whose parting surface is not flat.
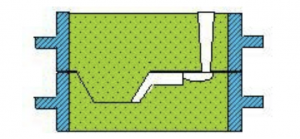
8) Fake box modeling
is to overcome the shortcomings of sand digging. Before modeling, make a bottom tire (i.e. fake box), and then make a box on the bottom tire. Because the bottom tire does not participate in pouring, it is called fake box. The operation is simpler than sand digging and the parting surface is neat. It is suitable for castings that require sand digging in batch production.
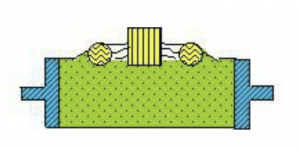
9) Split mold moulding
Split mold moulding is to divide the pattern into two halves along the largest section. The cavity is located in the upper and lower sand boxes, which is simple and labor-saving. Commonly used for castings with the largest section in the middle.
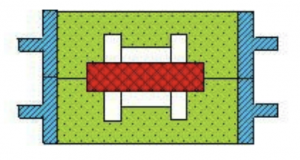
10) Live block modeling
Live block modeling is to make small bosses, ribs and other parts on the casting that hinder the ejection of the mold into activities (ie, live blocks). When drawing the mold, first take out the main body, and then take out the live block from the side. Its modeling is time-consuming, and workers have high technical requirements. It is mainly used for single-piece and small batch production of castings with protruding parts and difficult to mold.








Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!