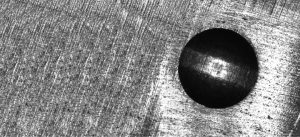
Brinell Hardness Test
Brinell Hardness Test
Test principle of Brinell hardness
The calculation formula of Brinell hardness is:
![]()
Among them, the unit of HB is kgf/
d——Indentation diameter, mm; h——Indentation depth, mm.
As long as the diameter of the indentation is measured, the HB value can be obtained by calculation or look-up table.
During the test, choose different loads and steel ball diameters according to the nature and shape of the material.
The advantages of the Brinell hardness test are strong representativeness, good data repeatability. At the same time, there is a certain conversion relationship with strength. The disadvantage is that harder materials cannot be tested; the indentation is large and not suitable for finished product inspection. It is usually used to test the hardness of raw materials and tempered parts, such as cast iron, non-ferrous metals, low alloy steel, etc.
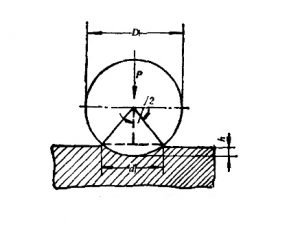
Test conditions
In the Brinell hardness test, we should select the diameter (D) of the indenter sphere, the test load (F), and the load holding time (t), according to the type of metal material, the range of hardness values and the thickness. There are five commonly used indenter diameters of 1, 2, 2.5, 5 and 10 mm.
The test load can range from 9.807N (1kgf) to 29.42 KN (3000 kgf).
The load holding time is generally 10-15s for ferrous metals; 30s for non-ferrous metals; 60s when the HB value is less than 35.
Pros and Cons
The diameter of the steel ball and the indentation left on the surface of the metal material is large. Therefore, the measured hardness value is more accurate. There is a certain relationship between HB value and tensile strength. That means we can determine the tensile strength of metal materials approximately according to the Brinell hardness value.
If the hardness of the metal is too high, it will affect the accuracy of the hardness value. Therefore, the HB test is generally suitable for measuring metal materials with a HB value of less than 650.
The Brinell hardness indentation is relatively large, so it is not suitable to measure finished products and sheet materials.
Yide casting is a leading casting foundry in China, we produce quality casting products, pursuing details required for every casting product, we have an imported testing machine to check the Brinell hardness and other parameters, committed to proving the best casting service for our casting customers.












 Due to the different materials, the distinction between cast aluminum and cast iron is quite obvious. Today, Yide Casting will share the differences with you, so that you can choose the right material for your castings.
Due to the different materials, the distinction between cast aluminum and cast iron is quite obvious. Today, Yide Casting will share the differences with you, so that you can choose the right material for your castings.